Written by Doug Short and Steven Hansen
Written by Doug Short and Steven Hansen
The Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index improved moderately after its decrease last month. The market expected this index to come in at 93.0 to 98.2 (consensus 95.5) versus the 101.3 reported.
This index has now improved to a point that its level is now commenserate with periods of economic expansion. Note that this data is considered preliminary, and the cutoff for these results was 19 March 2015.
Here is an excerpt from The Conference Board:
The Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index®, which had decreased in February, improved in March. The Index now stands at 101.3 (1985=100), up from 98.8 in February. The Expectations Index increased from 90.0 last month to 96.0 in March. The Present Situation Index, however, decreased from 112.1 in February to 109.1.
Lynn Franco, Director of Economic Indicators at The Conference Board, said: “Consumer confidence improved in March after retreating in February. This month’s increase was driven by an improved short-term outlook for both employment and income prospects; consumers were less upbeat about business conditions. Consumers’ assessment of current conditions declined for the second consecutive month, suggesting that growth may have softened in Q1, and doesn’t appear to be gaining any significant momentum heading into the spring months.”
Consumers’ assessment of present-day conditions turned moderately less favorable for a second straight month. The percentage saying business conditions are “good” was unchanged at 26.7 percent, while those claiming business conditions are “bad” increased from 16.7 percent to 19.4 percent. Consumers were mixed in their assessment of the job market. The proportion stating jobs are “plentiful” edged up from 20.3 percent to 20.6 percent, while those claiming jobs are “hard to get” also edged up from 25.1 percent to 25.4 percent.
Consumers’ optimism about the short-term outlook, which had declined last month, rebounded in March. The percentage of consumers expecting business conditions to improve over the next six months decreased slightly, from 17.6 percent to 16.7 percent; however, those expecting business conditions to worsen also fell, from 8.9 percent to 8.0 percent.
Consumers’ outlook for the labor market saw stronger gains. Those anticipating more jobs in the months ahead increased from 13.8 percent to 15.5 percent, while those anticipating fewer jobs declined from 14.8 percent to 13.5 percent. The proportion of consumers expecting growth in their incomes improved from 16.4 percent to 18.4 percent, while the proportion expecting a drop declined from 10.8 percent to 9.9 percent.
Putting the Latest Number in Context
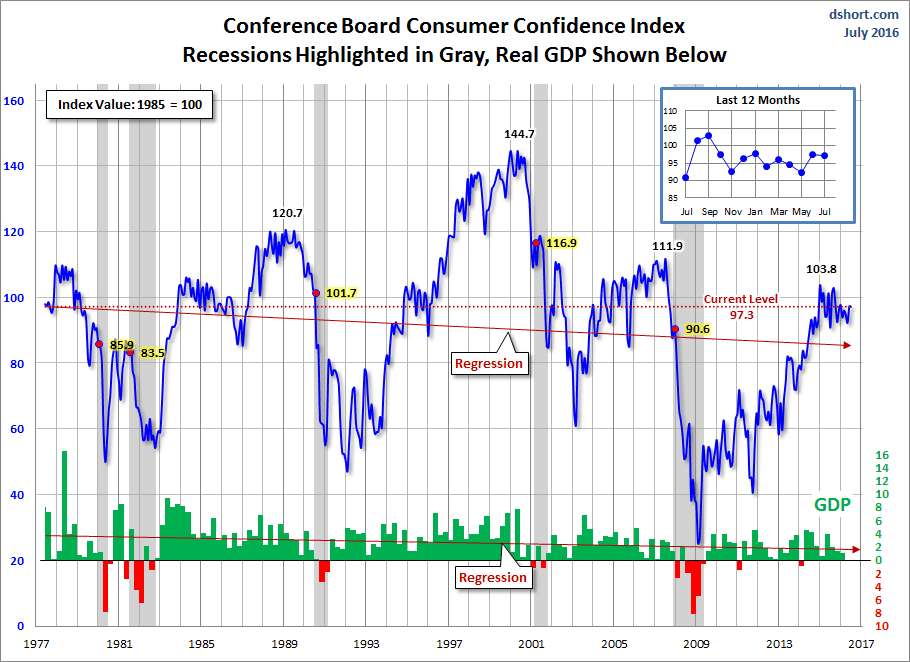
The chart below is another attempt to evaluate the historical context for this index as a coincident indicator of the economy. Toward this end I have highlighted recessions and included GDP. The regression through the index data shows the long-term trend and highlights the extreme volatility of this indicator. Statisticians may assign little significance to a regression through this sort of data. But the slope clearly resembles the regression trend for real GDP shown below, and it is a more revealing gauge of relative confidence than the 1985 level of 100 that the Conference Board cites as a point of reference.
On a percentile basis, the latest reading is at the 63rd percentile of all the monthly readings since the start of the monthly data series in June 1977.
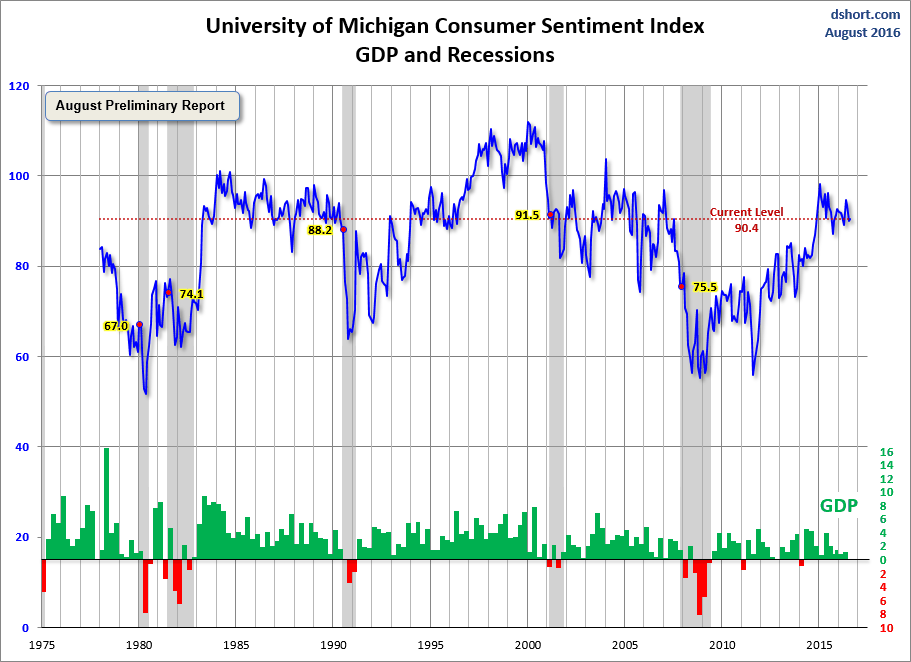
For an additional perspective on consumer attitudes, see my post on the most recent Reuters/University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index. Here is the chart from that post.
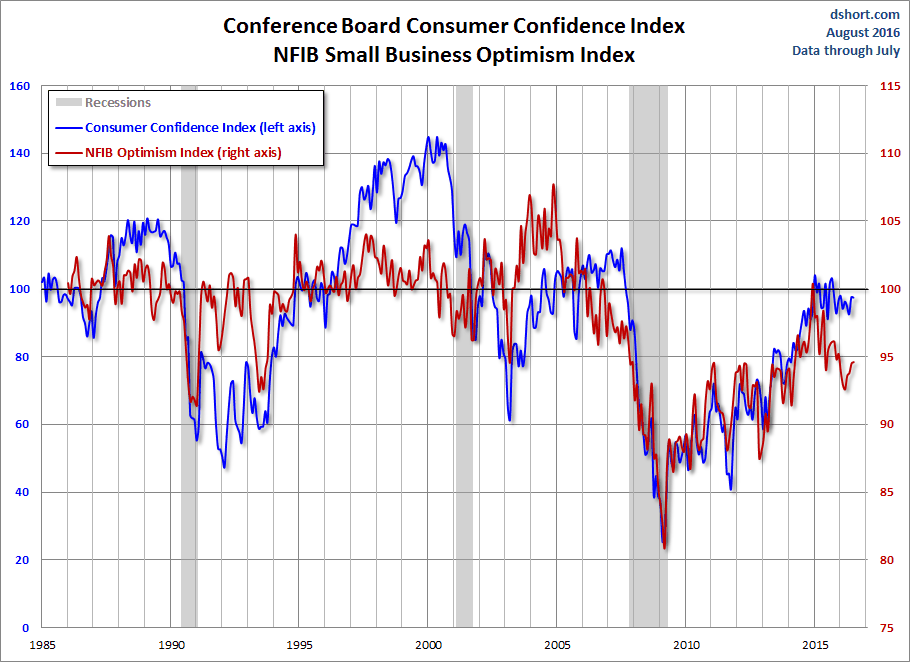
And finally, let’s take a look at the correlation between consumer confidence and small business sentiment, the latter by way of the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB) Small Business Optimism Index. As the chart illustrates, the two have tracked one another fairly closely since the onset of the Financial Crisis.
Caveats in Using the Conference Board’s Consumer Confidence Index
According to Bloomberg, the following caveat is provided when reviewing this series:
The underlying series for “planned purchases” (autos, homes, and major appliances) and “vacation intentions” showed larger increases in November 2010 levels, primarily due to sample design differences. These level shifts will be treated as breaks, and there will be no historial revisions. Neither series is included in or has any impact on the Consumer Confidence Index.The switch to the Census X-12 seasonal adjustment program produced only minor differences for both levels and month-to-month changes. As a result, The Conference Board did not find it necessary to undertake a full historical revision of the CCI time series based on the seasonal adjustment method. The restated data for November 2010, December 2010 and January 2011 (preliminary data) are based on the prior seasonal adjustment method. This index is an average of responses to the following questions: 1. Respondents appraisal of current business conditions. 2. Respondents expectations regarding business conditions six months hence. 3. Respondents appraisal of the current employment conditions. 4. Respondents expectations regarding employment conditions six months hence. 5. Respondents expectations regarding their total family income six months hence. For each of the 5 questions, there are three response options: Postive, Negative and Neutral. The response proportions to each question are seasonally adjusted. For each of the five question (above), the POSITIVE figure is divided by the sum of the POSITIVE and NEGATIVE to yield a proportion, which we call the ‘RELATIVE’ value. For each question, the average RELATIVE for the calendar year 1985 is then used as a benchmark to yield the INDEX value for that question. From 1967 to mid 1977 the CCI was bi-monthly.
This is a survey based on a probability-design random sample – conducted for The Conference Board by Nielsen. Surveys are a quantification of opinion rather than facts and data.
Observers of consumer sentiment polls should be aware they are imperfect quantifications of opinion. The question arises whether they are a rear view window or a forward looking indicator – or possibly a little of each. There is little question, however, that poor consumer sentiment corresponds to poor economic performance. Econintersect believes that consumer sentiment is mostly a coincident or lagging economic indicator.
Related Posts:
Old Analysis Blog | New Analysis Blog |
| Consumer Confidence | Consumer Confidence |
include(“/home/aleta/public_html/files/ad_openx.htm”); ?>