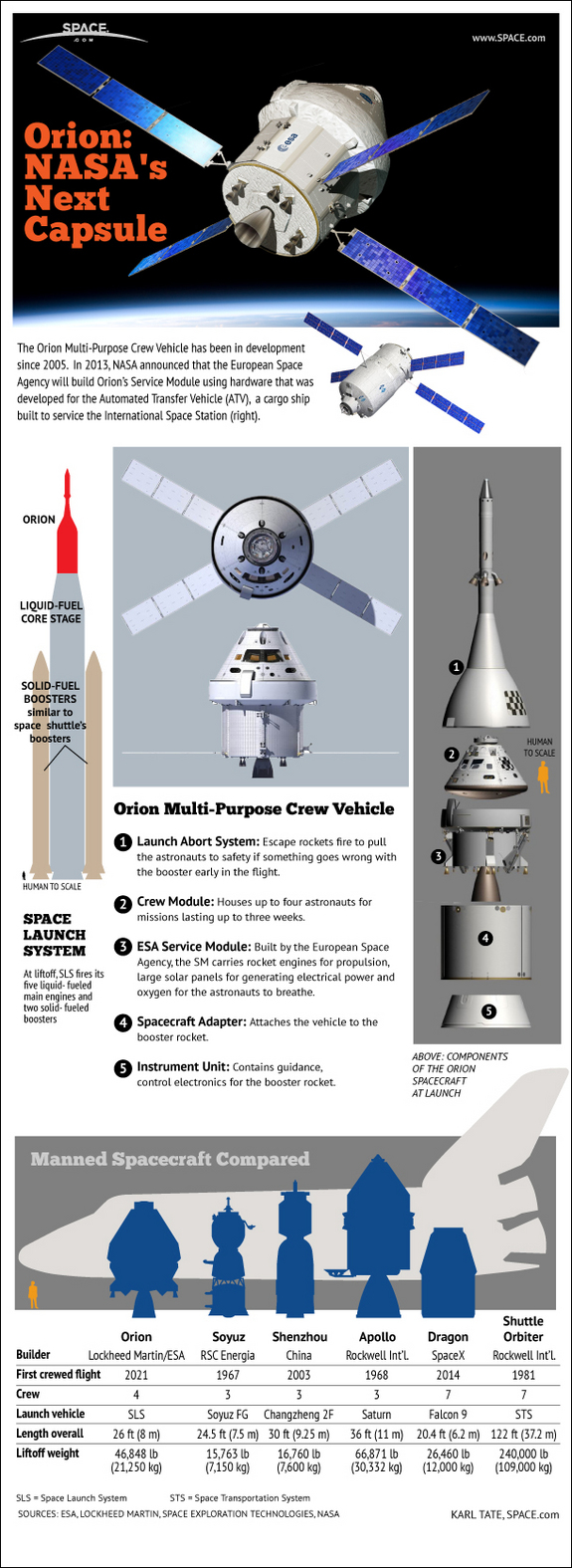
The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle will be America’s next manned spacecraft. The capsule has been in development since 2005. In 2013, NASA announced that the European Space Agency will build Orion’s Service Module using hardware that was developed for the Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV), a cargo ship built to service the International Space Station.
Source SPACE.com: All about our solar system, outer space and exploration
The Orion spacecraft has five main components. The Launch Abort System features escape rockets that fire to pull the astronauts to safety if something goes wrong with the booster early in the flight. [Photos: NASA’s Orion Space Capsule]
Orion’s Crew Module houses four astronauts for deep-space missions lasting up to three weeks.
The Service Module, built by the European Space Agency carries rocket engines for propulsion, large solar panels for generating electrical power and oxygen for the astronauts to breathe.
The Spacecraft Adapter is a set of panels for protecting the Service Module during the ascent through the Earth’s atmosphere.
An Instrument Unit contains guidance and control electronics for the booster rocket.
Orion will be launched on the Space Launch System booster. The vehicle features components evolved from those used in the Space Shuttle’s booster system. A central core stage has five liquid-fueled rocket engines. Strapped at the sides are large solid fuel boosters similar to the shuttle’s SRB boosters, but containing more fuel.
Orion’s first unmanned test launch is currently scheduled for 2017, with a crewed flight to follow in 2021.
- Photos: NASA’s Space Launch System for Deep Space Flights
- Crew-less Orion Capsule to Fly Around Moon in 2017 | Animation
- Where to See America’s Greatest Spaceships (Infographic)
source: Space.com








