Written by Steven Hansen
 The ISM Manufacturing survey for August 2014 continues to indicate manufacturing growth expansion with an moderate increase in the rate of growth.
The ISM Manufacturing survey for August 2014 continues to indicate manufacturing growth expansion with an moderate increase in the rate of growth.
The ISM Manufacturing survey index (PMI) rose from 57.1 to 59.0 (50 separates manufacturing contraction and expansion). This was well above expectations which were 55.8 to 58.5 (consensus 56.8).
This index had been in a general downtrend since mid 2011 – but now is trending up. This is the fifteenth month of expansion. The regional Fed manufacturing surveys were indicating growth in August, and now the ISM indicates manufacturing shows expansion in August also.

Relatively deep penetration of this index below 50 has normally resulted in a recession.
The noisy Backlog of Orders improved from 49.5 to 52.5 – and is now showing expansio. Backlog growth is an indicator of improving conditions; a number below 50 indicates contraction. Backlog accuracy does not have a high correlation against actual data.
Excepts from the ISM release:
Economic activity in the manufacturing sector expanded in August for the 15th consecutive month, and the overall economy grew for the 63rd consecutive month, say the nation’s supply executives in the latest Manufacturing ISM® Report On Business®.
The August PMI® registered 59 percent, an increase of 1.9 percentage points from July’s reading of 57.1 percent, indicating continued expansion in manufacturing. This month’s PMI® reflects the highest reading since March 2011 when the index registered 59.1 percent. The New Orders Index registered 66.7 percent, an increase of 3.3 percentage points from the 63.4 percent reading in July, indicating growth in new orders for the 15th consecutive month. The Production Index registered 64.5 percent, 3.3 percentage points above the July reading of 61.2 percent. The Employment Index grew for the 14th consecutive month, registering 58.1 percent, a slight decrease of 0.1 percentage point below the July reading of 58.2 percent. Inventories of raw materials registered 52 percent, an increase of 3.5 percentage points from the July reading of 48.5 percent, indicating growth in inventories following one month of contraction. The August PMI® is led by the highest recorded New Orders Index since April 2004 when it registered 67.1 percent. At the same time, comments from the panel reflect a positive outlook mixed with caution over global geopolitical unrest.
Of the 18 manufacturing industries, 17 are reporting growth in August in the following order: Plastics & Rubber Products; Furniture & Related Products; Fabricated Metal Products; Apparel, Leather & Allied Products; Wood Products; Printing & Related Support Activities; Miscellaneous Manufacturing; Paper Products; Petroleum & Coal Products; Food, Beverage & Tobacco Products; Nonmetallic Mineral Products; Chemical Products; Primary Metals; Transportation Equipment; Computer & Electronic Products; Machinery; and Electrical Equipment, Appliances & Components. The only industry reporting contraction in August is Textile Mills.

It is interesting to note that ISM Manufacturing represents less than 10% of USA employment, and approximately 20% of the business economy. Historically, it could be argued that the production portion of ISM Manufacturing leads the Fed’s Industrial Production index – however the correlation is not strong when looking at trends.
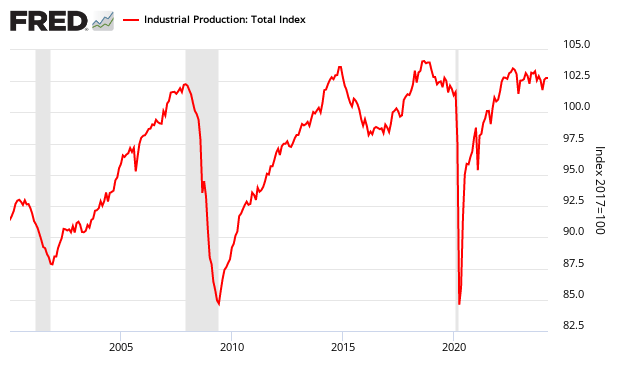
New orders have direct economic consequences. Expanding new orders is a relatively reliable sign a recession is NOT imminent. However, New Orders contraction have given false recession warnings twice since 2000.

However, holding this and other survey’s Econintersect follows accountable for their predictions, the following graph compares the hard data from Industrial Products manufacturing subindex (blue bar) and US Census manufacturing shipments (red bar) to the ISM Manufacturing Survey (purple bar).
Comparing Surveys to Hard Data
![]()


/images/z survey1.png
Caveats on the use of ISM Manufacturing Index:
This is a survey, a quantification of opinion – not facts and data. However, as pointed out above, certain elements of this survey have good to excellent correlation to the economy. Surveys lead hard data by weeks to months, and can provide early insight into changing conditions.
Many use ISM manufacturing for guidance in estimating manufacturing employment growth. Econintersect has run correlation coefficients for the ISM manufacturing employment and the BLS manufacturing employment data series above going back to 1988, using quarterly data. The coincident correlations are actually negative, but poor (r = -0.2 to -0.4 for various time periods examined). See here for definitions.
Before 2000 the ISM employment data had a weak positive correlation to the BLS data 4 to 7 quarters later (r values above 0.6). Since 2000 the correlations for ISM manufacturing employment as a leading indicator for the BLS manufacturing employment have been between 0 and 0.3 for r (correlation coefficient). These values define correlations as none to poor.
In other words, ISM employment index is not useful in understanding manufacturing jobsgrowth. The graph below shows BLS manufacturing employment month-over-month gains against the ISM Manufacturing employment index.
Indexed to Jan 2000 – Comparison of the ISM Manufacturing Employment Subindex (blue line) to BLS Manufacturing Employment (red line) – all data seasonally adjusted
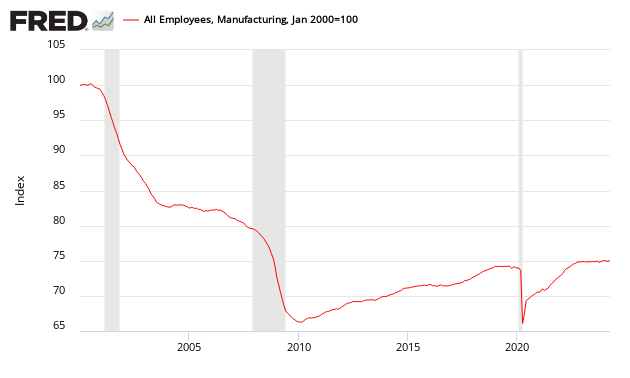
The ISM employment index appears useful in predicting turning points which can lead the BLS data up to one year.
Related Posts:
Old Analysis Blog | New Analysis Blog |
| Institute of Supply Management Surveys | Institute of Supply Management Surveys |







